As data continues to become crucial to all sorts of businesses, the need to understand, analyse, visualise, and use data grows more imperative.
However, without a data visualisation tool or analytics solution to view this data, businesses can quickly become overwhelmed. Data analytics solutions, business intelligence (BI) programs, and data visualisation tools are now essentials — rather than optional extras.
That’s why 54% of enterprises consider BI and other data-based solutions to be critical to their work now and in the future. By understanding the insights within their data, businesses can make better informed, data-driven decisions. But with a range of tools out there, which one is best?
In this blog, we’ll look at Looker, Power BI and Tableau — the three leading BI and data visualisation tools — to help decide which is best for you.
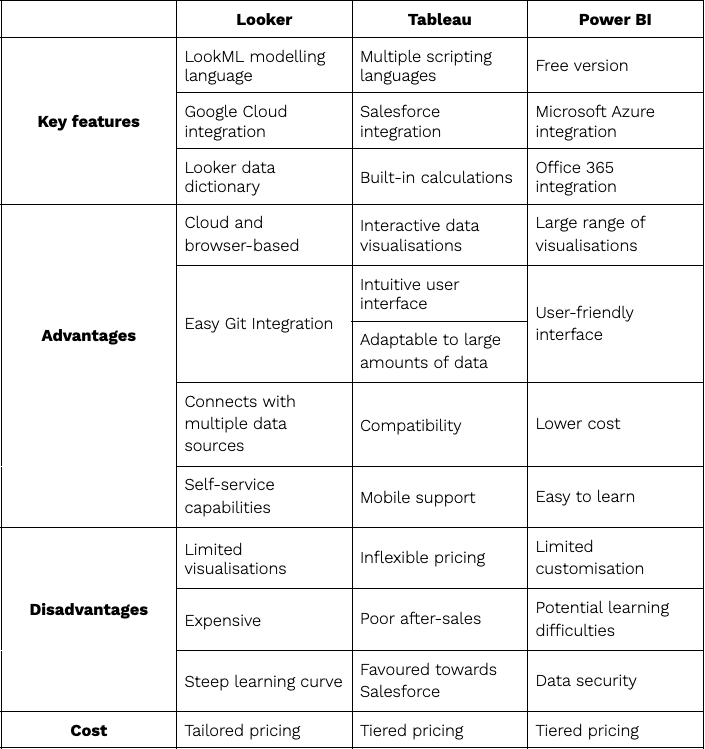
At a glance: Looker vs Tableau vs Power BI
Looker
Looker is a browser-based data analytics and visualisation tool. Founded in 2012, Looker was acquired by Google in 2019 and is now part of Google’s cloud platform. It also uses its own modelling language, LookML, a modular language that allows data and calculations to be reused. Alongside this, Looker’s Data Dictionary is a searchable directory for all metrics and descriptions in a Looker data warehouse.
Advantages
Looker’s unique approach to data offers some interesting advantages:
- Cloud-based & browser-based: Looker offers the useful combination of being part of Google’s Cloud Platform and being completely accessible via a browser. Google Cloud offers an advanced level of security and a flexible way to manage data. With direct access through a browser, these benefits are offered without the need for software installation and manual updates.
- Easy Git Integration: Looker can integrate with the popular version control system Git, enabling multiple people to work on multiple visualisations simultaneously. With Looker, users can see changes made to data-modelling layers, and jump back to them anytime. They can also create different version strands for developers to work on. This setup is easy and provides a benefit not offered by other data visualisation tools.
- Connects with multiple data sources: Looker integrates with more than 50 different data sources due to LookML, Looker’s data modelling language. LookML’s flexible modelling language means it can analyse and visualise data from multiple sources, including Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services and on-premises databases.
- Self-serve capabilities: LookML also offers the ability to define dimensions, metrics, aggregates and relationships. These can then be used seamlessly in data visualisations, providing self-service analytics whilst also enabling the data to be reused. Looker also offers an Explore feature that enables users to self-serve their data through drag-and-drop functions, individual dashboards, and the ability to add additional fields to aid in further data
Disadvantages
- Limited range of visualisations: Despite Looker’s popularity, the variety of visualisations offered with the basic program is somewhat limited. This comparison is even starker when comparing these capabilities to Looker’s competitors, Tableau and Power BI. It should be noted that Looker does offer the ability to build custom visualisations, which can go some way to mitigating this issue.
- More expensive than direct competitors: In theory, Looker’s pricing model is ideal with cost being tailored to the company in question. However, Looker is the most expensive of its competitors — Tableau and Power BI.
- Steep learning curve: Looker’s unique modelling language requires users to have at least a basic understanding of coding – in particular programming languages like SQL. The theory behind LookML is sound; a programming language that is easier to pick up. However, it is more difficult if a business lacks the right in-house expertise or training.
Looker’s ability to integrate with other systems, thanks to their unique LookML coding language, means that enterprise businesses can make use of data stored in already present third party software. Features like Looker Blocks — pre-built data models designed to fit common analytics patterns — streamline this integration, offering pre-built code that can more easily be embedded.
Looker is also a powerful beginner platform. Its systems are easy to learn, and the code is easily understood. While its visualistions might not be as sophisticated as its competitors, it also offers visualisation with real-time analysis and the ability to customise.
Tableau
Tableau formerly held the title of the undisputed king of Premium BI tools and has only recently gained rivals in Looker and Power BI. With quick implementation, ungoverned analytics and data can become accessible and easily shared throughout an organisation.
Tableau has recently been acquired by Salesforce, leading to simple integration with Salesforce users, as well as other programs such as MuleSoft and Slack.
Advantages
- Interactive data visualisations: Tableau provides interactive data visualisation benefits, helping to turn unstructured statistical information into logical and intuitive visualisations. Filtering and selection provide options for further analysis and ease of understanding.
- Adaptable to large amounts of data: Unlike other platforms that have a limit on data model size, Tableau has the ability to handle very large amounts of data without there being any impact on performance.
- Intuitive user interface: Developer and non-dev users alike can easily use Tableau due to its intuitive user interface (UI). Non-dev users can use all the basic facilities of Tableau, however, specialists might be needed to increase the platform’s functionality. Tableau’s simplicity is also coupled with its ability to reliably operate on big data thanks to its columnar data model.
- Compatibility: Tableau is compatible with multiple data sources, enabling businesses to connect with, access and blend data from multiple sources into one visualisation for easy data analysis. Tableau is also compatible with multiple scripting languages, such as Python or R, to maximise potential output.
- Mobile support: Tableau has a mobile app for both iOS and Android systems. This app has the same functionality as the desktop and online software, allowing users to analyse data remotely. Moreover, the Tableau dashboard can be customised to each application, meaning functionality can be maximised to the individual’s separate mobile and desktop needs.
Disadvantages
- Inflexible pricing: Tableau’s pricing doesn’t change on a case-by-case basis, despite the fact that most companies have individual needs. Purchasing an extended licence is required by Tableau’s sales model from the start. Many companies might find that they would rather start with a specific set of features and later adjust the pricing for further features if necessary.
- Poor after-sales support: Due to Tableau’s seniority, there are many online message forums that users can use to discuss Tableau’s features. However, many focus on a lack of support and maintenance. To resolve this, Tableau’s support team sometimes advise purchasing a new feature, which can become costly.
- Favoured towards Salesforce: Depending on an enterprise business’s requirements, this might not have a big impact. However, the nature of Salesforce’s acquisition means that Tableau’s development will now be skewed more towards Salesforce integration; Tableau is no longer an independent BI tool.
Tableau is designed with businesses in mind, rather than an IT department or developer. Tableau’s user interface is considered to be the easiest to use of its direct competitors. Its ease of usage means that you do not have to be an expert in programming languages or coding, empowering teams across an organisation to become more data-driven and data-literate in their decision making.
Power BI
Microsoft Power BI integrates well with Microsoft products and systems, however a recent uptick in adoption likely comes from the free version of Power BI that is available to anybody. This free version is reliable for individual analysts, but the premium version allows important functionalities such as sharing reports, dashboards or analytical apps.
Advantages
Microsoft’s tool offers the following advantages:
- Large range of visualisations: Power BI has a great number of standard visuals to populate your reports, each with a wide variety of format options. Power BI is backed up by integrations with Microsoft Office and can harness the power of Excel to create easy data visualisations. Moreover, if the desired option is unavailable, users can build their own custom visuals also.
- User-friendly interface: Power BI is extremely intuitive to navigate and user-friendly. Users with little dashboard experience can navigate the platform as easily as those with expertise. This is partly due to their natural language query tool, which allows people to ask simple questions to easily navigate to the data they wish to visualise.
- Lower cost: Power BI is relatively low in cost compared to other leading platforms. A trial version of Power BI is available to everyone, while Power BI Pro is included in some Office 365 business and enterprise plans. This has caused a shift in the market, causing other BI vendors to become much more competitive in their licensing options.
- Easy to learn: Power BI might be the easiest to use of the three platforms. Though you will need expert support to truly get the most of your data, those who are familiar with Excel will be able to start using Power BI’s data visualisation tools quickly.
Disadvantages
- Limited customisations: Though Power BI offers a range of visualisations to choose from, it can be difficult to customise any of them. There are basic formatting options available but this can prove limiting for businesses looking to create bespoke visualisations with limited Power BI experience.
- Potential learning difficulties: As covered, while Power BI is simple to get to terms with in the beginning, it will require added training further down the line. This especially applies when performing analysis over your datasets, as it will likely require tools that are external to Power BI, like DAX Studio.
- Data security: Power BI offers advanced encryption capabilities using Azure. However, as it’s a cloud-based tool, some stakeholders may feel uneasy about the security and privacy of their data. Businesses will have to ensure that they have the full breadth of knowledge of Power BI’s encryption services to fulfil their business case.
It’s clear that Power BI offers good integration capabilities, especially with other Microsoft products, allowing data analysis and visualisations to be shared across. It offers the reliability of other products, and even offers integrations into other data analytics tools.
Using a data consultancy to make the most out of your tools
Power BI, Tableau and Looker offer high-quality BI and data visualisation solutions for businesses in 2023. What is ‘best’ for your business is relative — but what’s not relative is that in order to maximise your ROI from these platforms and harness the power of your data, you need to get the best out of these tools.
Without in-house expertise or the right training, the steep learning curve and technical know-how required to maximise its potential can hurt your ROI, and squander the potential within your data. This is where Ipsos Jarmany can help.
With our consultancy services, we’ll help you find the right platform for your business. Once matched to the correct tool, we’ll help you maximise the insights you get from your data and make business intelligent decisions. Ipsos Jarmany’s team of data scientists are seasoned experts who understand that no two businesses have the same needs.
Whether you need help selecting a platform, getting the most out of data visualisations, creating a data strategy or something else, Ipsos Jarmany’s data consultancy experts can help.
Start a conversation today.